Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- docker
- wan
- instancenotfoundexception
- 우분투
- 백준
- springboot
- 디비서버활성화
- 배열빈도수
- 오라클멀티테넌트
- 도커
- jmx
- 도커권한설정
- ubuntu
- SpringApplication
- 배열최소값최대값
- 유니캐스트
- name=springapplication
- 네트워크모델
- 디비버
- dbeaver
- 리눅스계열
- 오름차순
- 포트포워딩 안될때
- Decapsulation
- 리눅스환경
- javax.management.instancenotfoundexception: org.springframework.boot:type=admin
- 모래시계출력
- 백준1946
- 배열복사
- 페이로드
Archives
- Today
- Total
다잘하고싶어
자바 객체직렬화 본문
☑️ 객체직렬화
- 객체를 저장하거나 네트워크로 전송하기 위해 연속적인 데이터로 변환하는 것
- 반대의 경우는 역직렬화( deserialization )
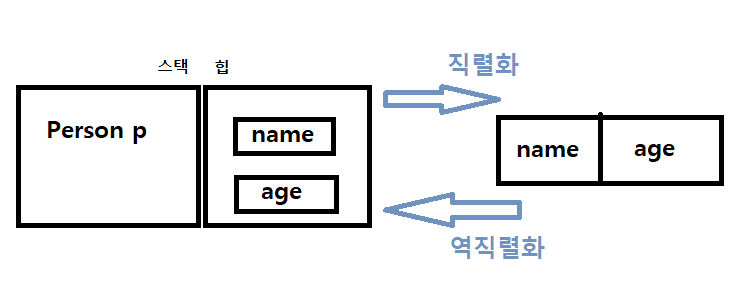
직렬화 조건
- Serializable 인터페이스를 구현할 것
- 클래스의 모든 멤버가 Serializable 인터페이스를 구현해야 함
- 직렬화에서 제외하려는 멤버는 transient 선언
클래스의 버전이 바뀌면(멤버변수, 메소드 변경..) 역직렬화 되어서는 안된다. 따라서 UID를 사용하여 직렬화 할때와 역직렬화 할 때 UID 가 동일한 경우에만 실행되도록 한다.
public class Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionId = 1L;


내가 읽고싶은 건? String 문자열
문자열을 바이트로 바꿔줘야함. data.getBytes() 이용
해결 코드
package test00;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SimpleInputTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleInputTest si = new SimpleInputTest();
si.read1();
}
String data = "hi java world";
void read1() {
try(InputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(data.getBytes())){
int read = -1; //없으면 -1 나온다고 했으니까 -1로 초기화
//더이상 읽을 것이 없을 때 까지 반복 수행
while((read = input.read()) != -1) { //한 바이트씩 읽겠다.
System.out.printf("읽은 값 : %d, 문자로 : %c\\n", read, read);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

package test00;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SimpleInputTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleInputTest si = new SimpleInputTest();
//si.read1();
si.read2();
}
String data2 = "자바는 객체지향 언어입니다.";
void read2() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
try(InputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(data2.getBytes())) {
int read = -1;
while((read=input.read(buffer)) > 0) {
System.out.printf("읽은 값 : %d, 문자로 : %s\\n", read, new String(buffer, 0 , read));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
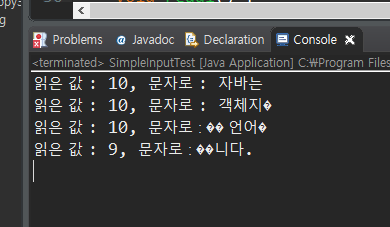
글씨가 깨지는 이유?
UTF-8 은 한 글자가 3byte
⇒ 해결하기 위해서는 buffer 의 배열크기를 키워주면 되지만, 용량을 무작정 지나치게 크게 설정할 수는 없다.
package test00;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.CharArrayReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.Reader;
public class SimpleInputTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleInputTest si = new SimpleInputTest();
//si.read1();
//si.read2();
si.read3();
}
String data2 = "자바는 객체지향 언어입니다.";
void read3() {
char[] buffer = new char[10];
try(Reader input = new CharArrayReader(data2.toCharArray())) {
int read = -1;
while((read=input.read(buffer)) > 0) {
System.out.printf("읽은 값 : %d, 문자로 : %s\\n", read, new String(buffer, 0 , read));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}


다른 운영체제에서도 잘 돌아가게 도와주는 용도의
File.separator → 클래스변수

true → 이어서 쓰겠다
false → 새로 쓰겠다.
정리
→ 객체들이 메모리 상에 연달아 있는 것이 아님
→ 전송하기 좋게 하기 위해서 연속적인 데이터로 만드는 과정—> 직렬화
연속적인 데이터로 만들어서 파일에 넣어버리겠다 ( 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 파일로 만들기)
→ 정리한 것들을 다시 풀어서 메모리에 올려서 우리의 것으로 쓰는 것을 역직렬화 라고 한다
Serializable 인터페이스
- 기능은 없음 + 구현해야하는 함수 없음.
- 이 클래스는 직렬화를 하고 있습니다 라는 표시
- serialVersinUID 생성..

파일생성됨


동적바인딩에 의해 찾아들어가서 Object.toString() 에서 person.toString() 을 찾아가서 Person~~ 이 나옴.
언제나 IDE( 이클립스) 를 기준으로 입력출력 생각하기
이클립스로 파일이 들어오면 입력( Input~)
이클립스에서 파일이 나가면 출력( output~)
package test07;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PersonListWriteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//리스트 자체를 객체로 생각하기
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Person("김가나", 28));
list.add(new Person("이가나", 25));
list.add(new Person("박가나", 23));
list.add(new Person("최가나", 120));
list.add(new Person("유가나", 55));
try (ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("personList2.dat"))) {
os.writeObject(list);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package test07;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class PersonListReadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream( new FileInputStream("personList2.dat"))){
List<Person> list = (List<Person>) ois.readObject();
for(Person p : list) {
System.out.println(p);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}




